Is the speed of light the speed limit of the universe? I believe that many people would give a positive answer to this question, because in the theory of relativity, the speed of light is the limit of the speed at which an object can move. However, this understanding is one-sided. In fact, the theory of relativity says that 1. The speed of motion of any object with rest mass cannot reach or exceed the speed of propagation of light in a vacuum (c); 2. The speed of transmission of any information or energy cannot exceed the speed of propagation of light in a vacuum.
In the framework of relativity, superluminal phenomena can exist as long as the above settings are not violated. For example, when light travels in water, its speed is only 75% of the speed of light in vacuum. In this case, we only need to accelerate an object moving in water to more than 0.75c to exceed the speed of light in water.
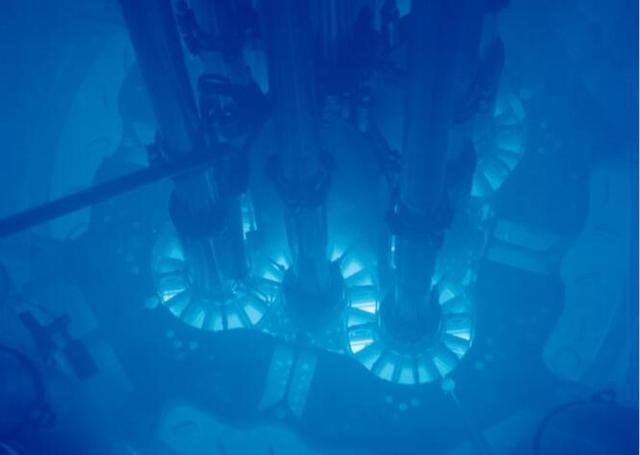

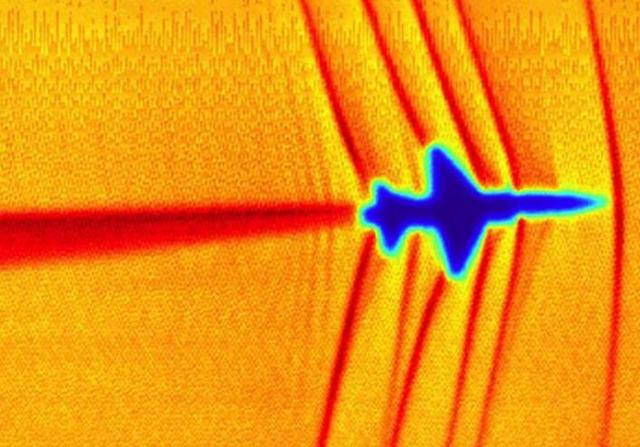
The blue glow in this picture is actually the result of some electrons gaining enough energy in the nuclear fission process that they move faster than the speed of light in the moderator, resulting in a "Light explosion " Phenomenon (similar in principle to a sonic boom).
Of course, this ftl is actually a significant reduction in the speed of light, and then to exceed it, which is a bit of a "Cheat" Suspicion, so is there any speed can directly exceed the speed of light in a vacuum? The answer is yes. In fact, the speed of light is not the speed limit of the universe, it is as slow as a snail compared to the following speeds.
The speed of expansion of the universe
According to astronomers' observations, the universe is in a state of accelerated expansion, as shown by the fact that for every 3.26 million light years of distance between two points in the universe, the speed at which they move away from each other due to the expansion of the universe increases by about 68 km/s.

Note that this speed is superimposable, meaning that if there is a galaxy 3.26 million light-years away from us, that galaxy will move away from us at about 68 km/s due to the expansion of the universe, galaxies 6.52 million light-years away from us will move away from us at about 136 km/s, and those further away will move away from us at an even faster speed.
It is easy to calculate that galaxies about 14.4 billion light years away are already moving away from us at the speed of light, galaxies 28.8 billion light years away are moving away from us at twice the speed of light, and if the universe is large enough, this speed will increase with distance and stack up to levels we can't even imagine.
The birth of the universe

The prevailing scientific view on the birth of the universe is the "Big bang theory", but this theory has faced some unexplained mysteries, so in 1980, scientists proposed the "Burgeoning universe theory" To explain the "Big bang theory". The "Big bang theory" Has been refined by scientists since 1980, and is now accepted by most scientists.
According to the "Burgeoning universe" Theory, the universe experienced a "Burst" Between 10^-35 and 10^-33 seconds after its birth, during which its size increased dramatically by a factor of 10^26 in a very short period of time. After this, the universe continued to expand, but at a much slower rate.
How fast is this "Surge"? Let's say that if the size of a region of the universe was 1 millimetre before the 'surge', then after the 'surge' that region would be 10^23 metres in size, which translates to about 10.57 million light years. In contrast, the speed of light cannot travel the radius of a single proton in this extremely short moment.
Quantum entanglement
Unobserved quanta are in a "Superposition state". For example, the spin of a particle can be clearly divided into up-spin and down-spin, but when it is in a "Superposition state", its spin becomes "Both up-spin and when it is observed, this "Superposition state" Collapses instantaneously and the spin of the particle is determined.
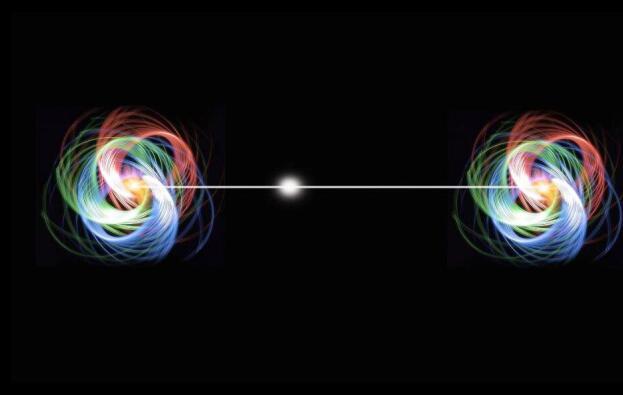
In quantum mechanics, when two particles in the "Superposition state" Form a special "Entangled state" After interacting with each other, scientists have found that the two particles in the "Entangled state" Have a special "Entangled state". Scientists have discovered that there is a mysterious connection between the two particles in the "Entangled state", and that once the state of one is measured, the "Superposition state" Of the other particle collapses instantly and its state is determined.
For example, if the spin of one particle is determined to be up-spin, the spin of the other is immediately determined to be down-spin.
What is even more amazing is that this connection is distance-independent; in theory, even if two particles in an "Entangled state" Are tens of billions of light years apart, once the state of one is determined, the other will instantly "Sense" The change in its if the state of one is determined, the other will instantly "Sense" The change of its "Companion" And will immediately change accordingly.
As you can see, compared to these speeds, the speed of light is a snail's pace. It should be noted that since the "Surge" And expansion of the universe are changes in space itself, and quantum entanglement cannot be used to transmit information, neither of them violates relativity.
(as soon as two particles in an "Entangled state" Are measured, the connection between them is immediately broken, and the "Superposition state" Is uncertain, so quantum entanglement cannot be used to convey information.)

The universe is so unimaginably large that even if humans were able to travel at infinitely close to the speed of light, they would not be able to penetrate its mysteries. Fortunately, the speed of light is not the speed limit of the universe, so it is entirely conceivable that in the distant future, humans may somehow be able to escape the shackles of the speed of light.